Electronic circuits are usually designed for a specific purpose, which means one circuit performs only one task, in general cases. This circuit here, “24-Hour Digital Clock and Timer Circuit” is a simple circuit with two different applications as reflected through the name 24-hour clock and a timer. The Circuit of a versatile 24-Hour Digital Clock and Timer Circuit is described below in detail. First, let’s go with some of its unique features.
Various Other timer and clock circuits are posted in bestengineeringprojects.com
- Industrial Timer Circuit
- Countdown Timer using Arduino
- Programmable Digital Timer Circuit
- Digital Clock with Second and Alarm Time Display
- Arduino Digital Clock using DS3231 Pi Module
Features of 24-Hour Digital Clock and Timer Circuit
- This circuit can be used for two purposes: both as a timer and a 24-hour clock.
- When using this circuit as a timer/an alarm. The time at which the device or load is to be switched ‘on’ or ‘off ‘ can be electronically stored while being displayed simultaneously.
- After storage of the time as mentioned above, the clock is set to display the real-time (in 24-hour mode) and it serves our purpose.
- Talking about the circuit components, it uses discrete ICs which are commonly available.
Circuit Description of 24-hour Digital Clock and Timer Circuit
The entire circuit can be divided into two main parts.
- A 24-hour digital clock circuit.
- Preset time storage, comparator, and relay driver circuit.
A 24-hour digital clock circuit.
Fig. 1. shows the circuit of the 24-hour digital clock section. This section is designed to display the time in hours and minutes format and is wired such that it functions in 24-hour mode. For this purpose, this circuit makes use of six 74LS90 decade counters (in the figure, IC1 through IC6), four 74LS247 BCD to 7-segment decoders/drivers (IC7 through IC10), and four LT S542 common anode displays (DIS1 through DIS4). In addition, passive components like few resistors, capacitors, and push-to-on switches are employed. A 1Hz clock is used to supply the input to the IC1 through pin 14. 1 Hz clock generator circuit is shown in the button of the article. The output obtained from both of the above-mentioned circuits become more accurate with the fact that both circuits take advantage of 32.768kHz quartz crystal.
Description of Counter Circuit
Each ICs are designed/wired with a particular task to perform. During this course, IC1 serves as a divide-by-10 counter and IC2 as a divide-by-6 counter. Thus the output of IC2 connected to clock pin 14 of IC3 has a pulse recurrence period of one minute. Similarly, following the connection pattern of IC1-IC2, the IC3-IC4 pair is wired likewise. And, so the output of IC4 connected to clock pin 14 of IC5 has a pulse recurrence frequency of one hour. IC pair 5 and 6(IC5-IC6) is set such that it resets themselves on reaching a count of 24. The BCD to 7-segment decoders IC7 through IC10 is used to decode the BCD outputs of IC3 through IC6. In response to this, the 7-segment common-anode displays DIS1 is driven through DIS4 respectively.
The clock gets reset at 24 hours count and for this reason, the maximum time that would be displayed by the clock is 23 hours and 59 minutes. The BCD outputs of IC3 through IC6 marked A1 through A4, B1 through B4, C1 through C4, and D1 through D4 respectively, are also connected to various IC pins (Fig. 4) bearing identical markings. Circuit noise can rise as a major problem in the operation. To solve this, Decoupling capacitors of 0.1µF each have been used between Vcc and ground of all ICs.
We can see in the figure, that the 1Hz clock is also connected to one of the poles of push-to-on switches S1 and S2. These switches are used for quick adjustment of minutes and hours count respectively. With this arrangement of switches, the clock can be set to display any desired time between zero hours and zero minutes to 23 hours and 59 minutes.
Preset time storage, comparator, and relay driver circuit.
The circuit design of the second part is clearly illustrated in fig.2. which comprises preset time storage, magnitude comparator, and relay driver part. Major components of this circuit can be enlisted as two 74LS373 octal ‘D’ type transparent latches (IC11 and IC12), four 74LS85 4-bit magnitude comparators (IC13 through IC16), one 74LS21 dual 4-input AND gate (IC17), and Darlington pair comprising transistors BC547 (T1) and SL100 (T2). Each nibble (4-bit sequence) of BCD data from IC3 through IC6 of the first part of the clock circuit is connected to IC11 and IC12 (two nibbles to each of these ICs). The reason behind doing so is to latch (store) by momentary depression of press-to-on switch S3.
The latched nibbles are connected as one set of 4-bit data inputs to magnitude comparator ICs 74LS85, while the other set of 4-bit data (BCD output from IC3 through IC6) are directly connected to comparators as shown in Fig. 4. These nibbles directly connected and latched ones are compared. When all four nibbles of stored/latched data equal the directly connected four nibbles of data, pin 6 of all 74LS85 ICs goes to logic 1 state. This results in pin 6 of 4-input AND gate of IC17 going high and then energizes relay RL 1 via Darlington pair comprising transistors T1 and T2. For further clarification of the operation procedure, one must go through the following description.
Operation Of 24-Hour Digital Clock and Timer Circuit
The desired pre-setting time for the load or appliance to be switched ‘on’ or ‘off ‘ is carried out with the help of switches S1 and S2 by looking at the digital display. Switch S3 is pressed briefly, once the display shows the desired time. IC11 and IC12 are used to store time just programmed. This latched time appears as one of the BCD inputs at each of the four comparator ICs (IC13 through IC16). Now using the same switches (S1 and S2), the current time is set.
Similarly, the BCD equivalent of the current time appears as the second set of inputs for IC13 through IC16. The current time (real-time) keeps advancing since the 1Hz input continuously updates the clock/timer. After a certain interval, time reaches the maximum limit. Once the current time reaches the preset time, both sets of input BCD numbers to 74LS85 comparator ICs become equal and this sets pin 6 to reach the logic 1 state. As a result, the output of AND gate (IC17) goes to the logic 1 state and energizes relay RL 1 via the Darlington pair of transistors Tl and T2 as stated earlier in the circuit description.
The CD value at the output of IC3 changes after each minute and therefore, this state persists for a while. To keep the relay continuously energized on reaching the preset time. The relay is latched by grounding the bottom end of the relay through a normally open, second set of contacts of the same relay. In that case relay with two changeover contacts should be used for RL1.
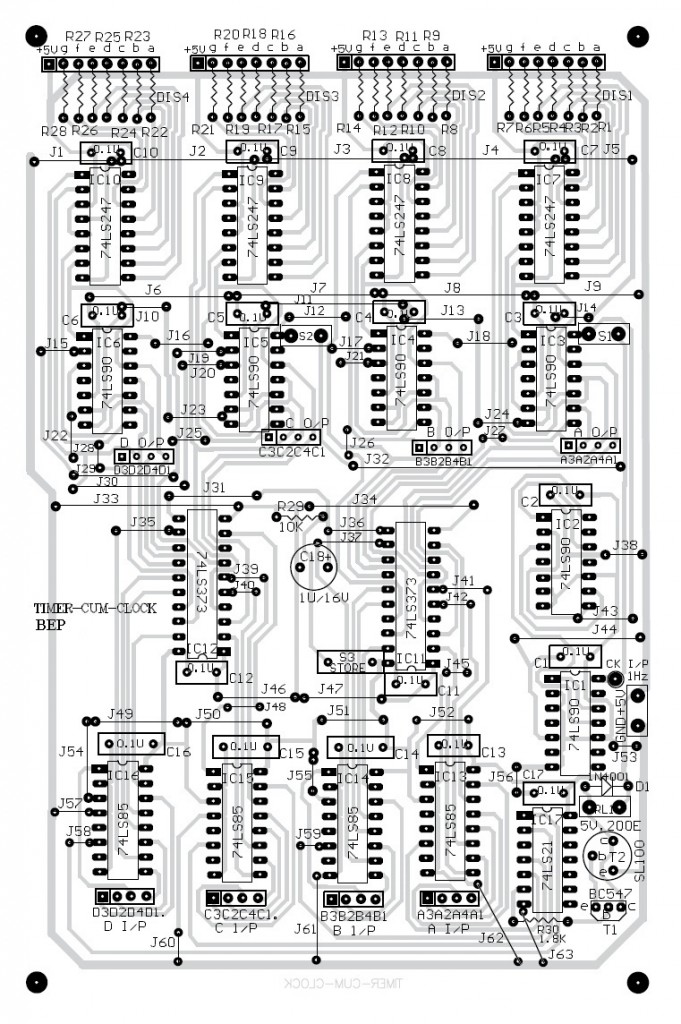
PCB Design for 24-Hour Digital Clock and Timer Circuit
Fig, 2 shows the actual-size, single-sided PCB for the circuits of Figs 1 and 4. And, the components layout for the PCB is shown in Figure 3. We can connect the 7-segment digital displays on the front panel using a suitable general-purpose PCB. This can be done by extending the segment outputs using ribbon cables and SIP connectors. Any 5-volt regulated DC power supply capable of sourcing about one ampere of current can be used with this circuit. We can retrieve extra benefits from the circuit. Since the power supply as well as 1Hz generator can also be wired on general-purpose PCBs and mounted suitably within the same enclosure.
Figure: 2 Solder Side PCB Design For Figures 1 And 4;
Figure 3: Component Side PCB Board for Figures 1 and 4;
However, we should note that BCD outputs of the four counter ICs (IC3 through IC6) have been terminated on SIP connectors in the PCB. These outputs are to be extended to IC13 through IC16 using SIP connectors and ribbon cables.
PARTS LIST OF 24-HOUR DIGITAL CLOCK AND TIMER CIRCUIT
| Resistors (all ¼-watt, ±5% carbon, unless stated otherwise): |
| R1 – R28 = 560 Ω
R29 = 10 KΩ R30 = 1.8 KΩ |
| Capacitors |
| C1 – C17 = 0.1 µF Caramic Disc
C18 = 1 µF/16V Electrolytic Capacitors |
| Semiconductors |
| IC1 – IC6 = 74LS90 (Decade Counter)
IC7 – IC10 = 74LS247 (BCD to 7-Segment Decoder/Driver) IC11, IC12 = 74LS373 (Octal D-type transparent latches) IC13 – IC16 = 74LS85 (4-bit magnitude comparator) IC17 = 74LS21 (dual 4-input positive AND gate) T1 = BC547 NPN Transistor T2 = SL100 NPN Transistor D1 = 1N4001 Rectifier Diode |
| Miscellaneous |
| DIS1 – DIS4 = FNDLTS542 (common anode display)
SW1 – SW3 = PUSH-TO-ON Switch RL1 = 5V, 200 Ω Relay |




Dear sir,coagulation, I am very interested on electronic subject,but I can’t learning it.I hope on this time I will teaching.please you help me.thanks.
Dear Sir please you takeme for same learn.actually before I don’t know same this subject.
thanks.
we want timer for tower to start relay
what is a 1Hz clock
what is the component name for the 1Hz clock
here are the list of various clock generating circuit, you can choose any one from these list.
http://bestengineeringprojects.com/clock-signal-generator-circuit/
Thank you sir, so only the Vout should connected to pin 14 of the IC 1…. And the 1Hz clock circuit should have a different source..?
yes, you can directly connect 1Hz output to pin 14 of IC1
Sir, the source of the 1Hz clock is the same source as to the whole 24 hour digital clock circuit?
Sir, is voltage source of the 1Hz circuit is as the same as the voltage source of the whole 24 hour digital circuit..?
I had updated the article 24-hr digital clock and timer circuit with 1Hz clock generator circuit.
Thank you
Thank you
Sir the voltage source of the 1Hz circuit is connected to the voltage source of the whole 24 hour digital circuit..?
Wait for a day i will design a simple 1 Hz clock pulse generator.
What is RV1 in 1Hz circuit, is it a resistor?… Do you have a finish product on this project..? if you have please send a picture or maybe a video.. Thank you
Good day sir, is the C1 10 microfarad electrolytic in the 1Hz pulse generator and RV1 is it a resistor..?
Yes c1 is electolytic
Rv1 is variable resistor.
sir is it possible to not include figure: 2 latch/storage.. only the figure:1 will be made.
Do you have a PCB layout for Figure 1 only? the clock only
Sorry, we don’t have PCB design of Figure 1 only. but you can try another circuit http://bestengineeringprojects.com/digital-clock-with-seconds-and-alarm-time-display/
can we make only 24 hour clock (And not the timer circuit)?
There is already Digital clock with alarm time display circuit.
http://bestengineeringprojects.com/digital-clock-with-seconds-and-alarm-time-display/
can we make it with this circuit only? (figure 1, I mean)
You list 2 transistors and a relay in your 24 hour timer, but in your diagram
they are not present. A real waste of time.
Please go through the article, in figure 2 of circuit you can see the two transistor with a relay.
Hi, thaks for your circuit is very interesting do it by my self this kind of circuit, just for lear, so i made it but just in a simulator and work very fine (now a searching the componets for made the real prototype), but there is somethig that i dont understand, i just can store just one desire hour, and i can´t activate the relay for more than one minute because ic3 change every minute…what can i do for activate the relay for example one hour or 30 minutes? could you teach me please?